Advanced IVF, Personalized for You
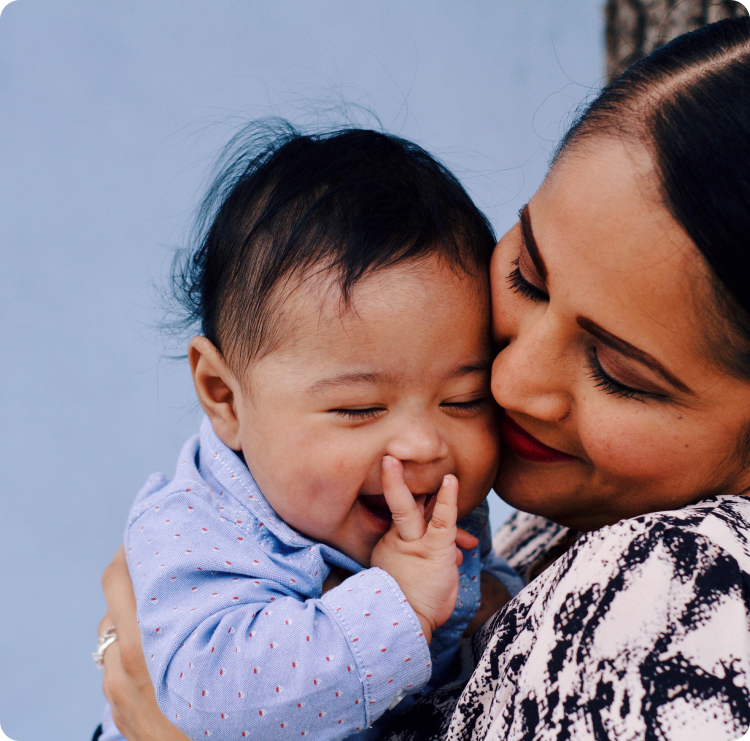
At Bay IVF, we offer state-of-the-art In Vitro Fertilization — with a human touch, fewer visits, and a plan built around your life and your goals.


IVF is the most effective fertility treatment available for many patients — especially when other treatments haven’t succeeded or when conditions like male-factor infertility, tubal blockage, endometriosis, or diminished ovarian reserve are involved.
At our Palo Alto clinic, we’ve refined IVF protocols to be as comfortable and efficient as possible, helping you stay engaged in life while we support your journey.
Is IVF Right for You?
We’ll review your history and test results and help determine whether IVF (or a tailored variation) is the best step for your unique situation.

- You have a tubal blockage or pelvic adhesions.
- You have male factor infertility.
- You have infertility associated with endometriosis.
- You have infertility associated with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS).
- You have unexplained infertility.
- You have diminished ovarian reserve.
- You are 37 years or older.
Our Approach – Gentle, Expert, Personalized
Gentle stimulation, not excessive. We emphasize egg and embryo quality over sheer quantity — which means fewer medications, fewer visits, and less stress for you.
Personalized treatment. Dr. Polansky and our small, dedicated team will build your plan. You’re never just another cycle number.
Minimized disruption.
Many patients can continue their daily lives during treatment thanks to our streamlined protocols.
Transparent and supportive. From costs to timeline, you’ll know what to expect — and we’ll be available every step of the way.



Our goal is to make your conception experience pleasant, relaxed, and as natural as possible.
What Does the IVF Process Look Like?

Ovarian stimulation
A personalized stimulation schedule begins, with monitoring (blood work & ultrasounds) to optimize egg development.

Fertilization of eggs
Evidence of fertilization can be seen the next day. The fertilized eggs are then transferred into a growth medium and cultured in our laboratory.
Egg retrieval
A brief, outpatient procedure under sedation. Our team ensures comfort and safety.

Culture of embryos
Your eggs are retrieved, combined with sperm (or ICSI is done when indicated)
Embryo transfer
One or two embryos are placed into the uterus via a catheter — usually a quick and comfortable procedure.
Embryo implantation
We follow you through to your blood test and ultrasound milestone, and then coordinate hand-off to your OB/GYN if pregnancy is confirmed.
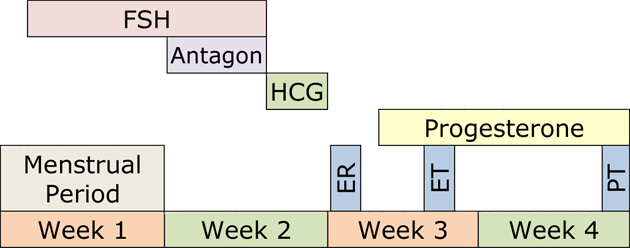
Below is an example of an IVF treatment cycle. Your individualized protocol may take less or more time to complete.

What Matters Most for Success
Your chances hinge on the following three key factors.

- Your fertility potential (especially egg quality and ovarian reserve)
- Quality of the laboratory and the embryology team
- Optimized stimulation and an appropriate protocol for your body



Bay IVF Success
At Bay IVF, over 60% of IVF cycles for patients under 35 lead to a live birth.
(Based on the 2024 SART data.)

Your First Step with Us
Your journey starts with a conversation. We’re here to support you every step of the way.

- Call or text us at 📞 650 322 0500 to schedule your in-person or a complimentary video consultation with Dr. Polansky.
- You will discuss your history, goals, and concerns.
- Review what IVF might look like for you, including timeline, visits, and cost.
- Receive a personalized roadmap — no obligation, just honest guidance.
Bay IVF Early Pregnancy Heartbeat


Treatment Prerequisites
Only a few treatment prerequisites are required before your treatment begins. They assess the egg and sperm quality and ensure that embryos can be accurately placed in a healthy uterus.
Female partner’s age
The probability of a successful IVF treatment declines sharply after age 44. You must be 43 and 11 months or younger at the time your IVF treatment begins. Patients who are 44 and older should strongly consider Donor Egg IVF as the most effective treatment option to achieve a successful pregnancy.
Female partner’s weight
Your BMI must be no greater than 31 for an adequate ovarian response and safety during the egg retrieval procedure. If your BMI is higher, please follow the IVF Diet and Lifestyle (PDF) recommendations as closely as possible. By doing so, you can achieve weight loss at an optimal rate, which could significantly improve your chances of a successful pregnancy.
Pathogen testing
This testing is required by the State of California. You and your partner (if applicable) must be tested for Hepatitis B-Surface Antigen, Hepatitis C-Antibody, HIV I&II, HTLV I&II (male partner only), and RPR.
Ovarian Reserve Assay (ORA)
ORA assesses the likelihood of producing normal-quality eggs. It involves measuring Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH), estradiol (estrogen, E2), and Anti-Mullerian Hormone (AMH) levels in blood.
These test results are used to optimize ovarian stimulation.
Antral Follicle Count
The number of antral follicles (small fluid-filled sacs within the ovaries seen on ultrasound) in unstimulated ovaries is related to the quality of the eggs. Ideally, there should be approximately 20 antral follicles in both ovaries combined.
Uterine measurement and saline ultrasound
It is important to determine the length of the uterus to ensure proper embryo placement.
Saline ultrasound is used to rule out intrauterine polyps or fibroids.
Semen evaluation
The male partner’s semen will be evaluated at Bay IVF to determine the best laboratory method for semen preparation for egg insemination.
Parents’ genetic testing (optional)
All prospective parents should consider genetic screening for hundreds of the most common genetic diseases. Please inform us during your initial appointment at Bay IVF if you would like to have your blood sample sent for genetic screening.
IVF diet and lifestyle
Environmental factors significantly impact reproductive health. Please review the IVF Diet and Lifestyle document (PDF) for a comprehensive list of environmental reproductive health recommendations and a source for dietary supplements.



Let’s Begin This Journey Together
Your first conversation is free — no pressure, just real answers from people who care.
Call us today to speak directly with our team and take your first step toward growing your family.
Meet Your Doctor
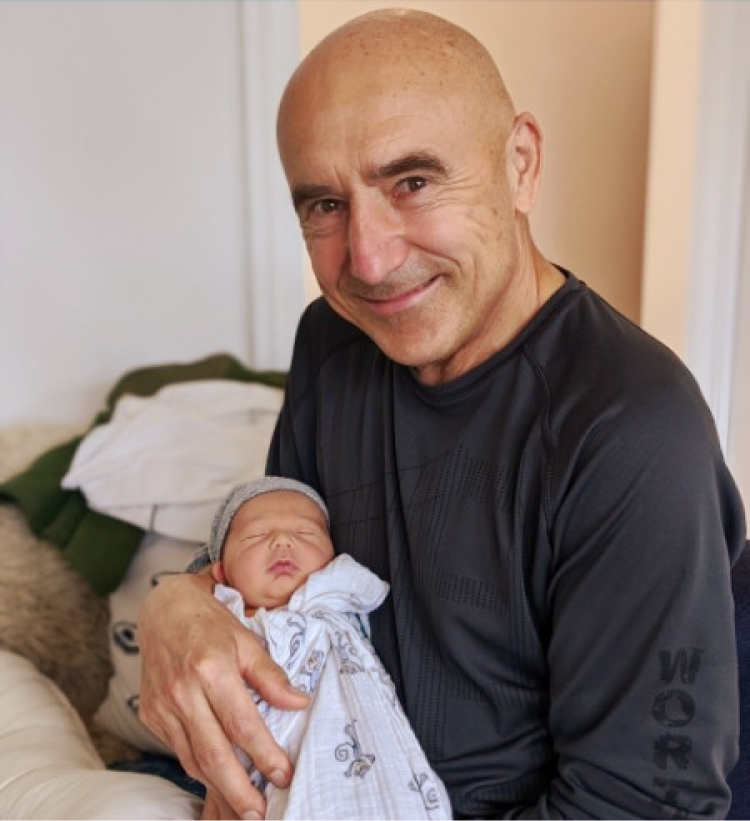

- Dr. Polansky received his medical diploma from Charles University in Prague, the Czech Republic, in 1978.
- After completing his OB/GYN residency at Jewish Hospital in Saint Louis, MO, he graduated from the Reproductive Endocrinology and Infertility (REI) fellowship at Stanford University in 1985.
- In the same year, he co-founded the Stanford IVF Clinic.
- Dr. Polansky obtained board certification in Obstetrics and Gynecology in 1986 and became REI subspecialty board certified in 1988.
- In 1987, he left Stanford University and established Nova IVF.
- In 2011, he founded Bay IVF, where he provides advanced fertility treatments with a holistic approach, utilizing state-of-the-art techniques.
- Dr. Polansky personally performs ultrasound examinations, egg retrievals, embryo transfers, and ovarian and endometrial stimulations for his patients.
- He is deeply committed to his patients and is always ready to lend a helping hand.
Frank Polansky, M.D.


Initial Appointment Questions
When you call to schedule your consultation, one of our Front Office Coordinators will ask you a short series of simple questions regarding your reproductive history. You will also have an opportunity to ask any financial questions.
Your Initial Visit at Bay IVF
A new patient appointment at a fertility clinic can be stressful. Our goal is to make your initial visit as friendly and relaxing as possible. We encourage you to ask questions at every step of the process to make you feel comfortable and informed.

When You Arrive
You will be welcomed by one of the clinic’s receptionists. One of our nurses will measure your height and weight and take your blood pressure.

Meet Your Doctor
Dr. Polansky will ask you a series of clarifying questions and then provide you with a summary of the factors contributing to your infertility.

Ask Your Questions
You will then have a discussion with him about the most suitable reproductive treatment(s) for you. During this time, you will have the opportunity to ask any questions you may have.

Exam Room
One of the nurses will escort you to an examination room. Your examination will begin with listening to your lungs and heart.

Ultrasound of the Ovaries
The next step is a pelvic ultrasound to examine the uterus and ovaries. This ultrasound will help determine the number of antral follicles present within the ovaries.

Financial Part
After that, you will discuss the financial aspects of your treatment with one of the financial advisors, including potential financing options.

Support 24/7
If you have any questions after leaving the clinic, please feel free to reach out to us by phone, text, or email. Open and discreet communication is an integral part of the care we provide at Bay IVF.

What About Time?
Your entire visit is expected to last approximately one hour.

Schedule Your Initial Consultation With Dr. Polansky
Online (no cost) or In-Person
Call or Text Us: Call or text us at 📞 650 322 0500
You can also complete the form below to request your initial consultation.


Let’s talk about your next step